You are given a string s, an integer k, a letter letter, and an integer repetition.
Return the lexicographically smallest subsequence of s of length k that has the letter letter appear at least repetition times. The test cases are generated so that the letter appears in s at least repetition times.
A subsequence is a string that can be derived from another string by deleting some or no characters without changing the order of the remaining characters.
A string a is lexicographically smaller than a string b if in the first position where a and b differ, string a has a letter that appears earlier in the alphabet than the corresponding letter in b.
Input: s = "leet", k = 3, letter = "e", repetition = 1 Output: "eet" Explanation: There are four subsequences of length 3 that have the letter 'e' appear at least 1 time: - "lee" (from "leet") - "let" (from "leet") - "let" (from "leet") - "eet" (from "leet") The lexicographically smallest subsequence among them is "eet".
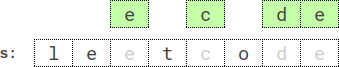
Input: s = "leetcode", k = 4, letter = "e", repetition = 2 Output: "ecde" Explanation: "ecde" is the lexicographically smallest subsequence of length 4 that has the letter "e" appear at least 2 times.
Input: s = "bb", k = 2, letter = "b", repetition = 2 Output: "bb" Explanation: "bb" is the only subsequence of length 2 that has the letter "b" appear at least 2 times.
1 <= repetition <= k <= s.length <= 5 * 104sconsists of lowercase English letters.letteris a lowercase English letter, and appears insat leastrepetitiontimes.
impl Solution {
pub fn smallest_subsequence(s: String, k: i32, letter: char, repetition: i32) -> String {
let k = k as usize;
let repetition = repetition as usize;
let mut remain = s.chars().filter(|&c| c == letter).count();
let mut count = 0;
let mut stack = vec![];
for (i, c) in s.chars().enumerate() {
while *stack.last().unwrap_or(&'a') > c && s.len() - i + stack.len() > k {
if *stack.last().unwrap() == letter {
if count + remain > repetition {
count -= 1;
} else {
break;
}
}
stack.pop();
}
if c == letter && count + remain == repetition && stack.len() + remain >= k {
while stack.len() + remain > k {
remain += (stack.pop().unwrap() == letter) as usize;
}
stack.append(&mut vec![letter; remain]);
break;
}
if stack.len() < k {
count += (c == letter) as usize;
stack.push(c);
}
remain -= (c == letter) as usize;
}
stack.into_iter().collect()
}
}